Divers map Scapa Flow wrecks ahead of centenary in 2019 BBC News

Digital Past 2013
A centrepiece of the Scapa Flow Wrecks website is the interactive 3D shipwrecks of the seven remaining German High Seas Fleet wrecks. These allow the general public to delve beneath the surface, offering a unique and fascinating insight into the shipwrecks resting on the seabed of Scapa Flow today.

Scapa Flow wrecks how the scuttling of the German fleet after WWI crafted the Orkney diving
Scapa Flow is a naturally protected bay in the Orkney Islands, to the north of mainland Scotland. The topography of the islands means it's been used as a base for navies dating all the way back to the Vikings in the 11th century. More recently, Scapa Flow served as the main base for the British Navy during the First and Second World Wars.

Scapa Flow Wrecks Geophysical Survey Our Work Wessex Archaeology
Divers have mapped several Scapa Flow wrecks ahead of the centenary in 2019 A detailed record of German warships scuttled in Scapa Flow has been created in preparation for the centenary of.
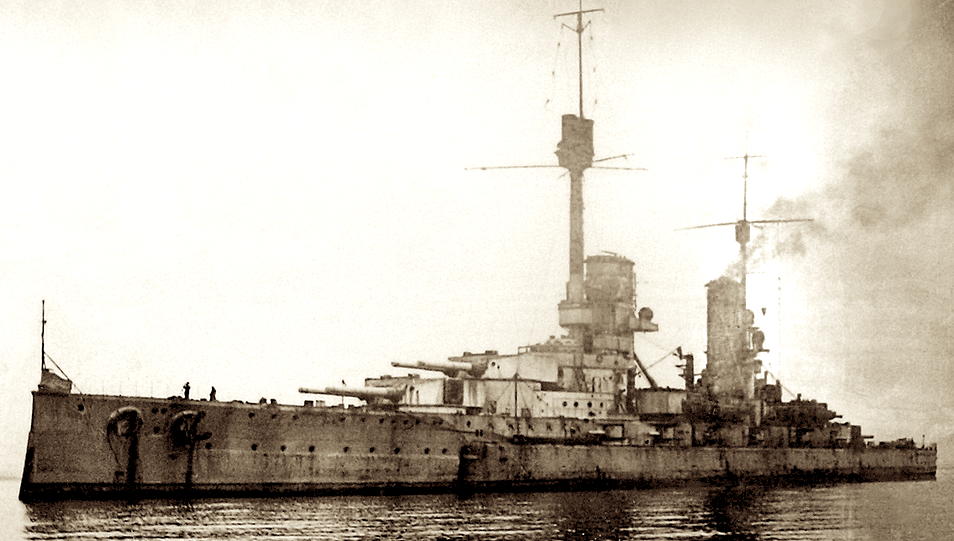

Four Scapa Flow German wrecks sell online The Orcadian Online
Scapa Flow is a natural bay, sheltered from the wind, located in the Orkney Islands. This port was used as naval base for the Royal Navy during both world wars. In November 1918, a few days after the Armistice, Germany is forced to surrender all warships.
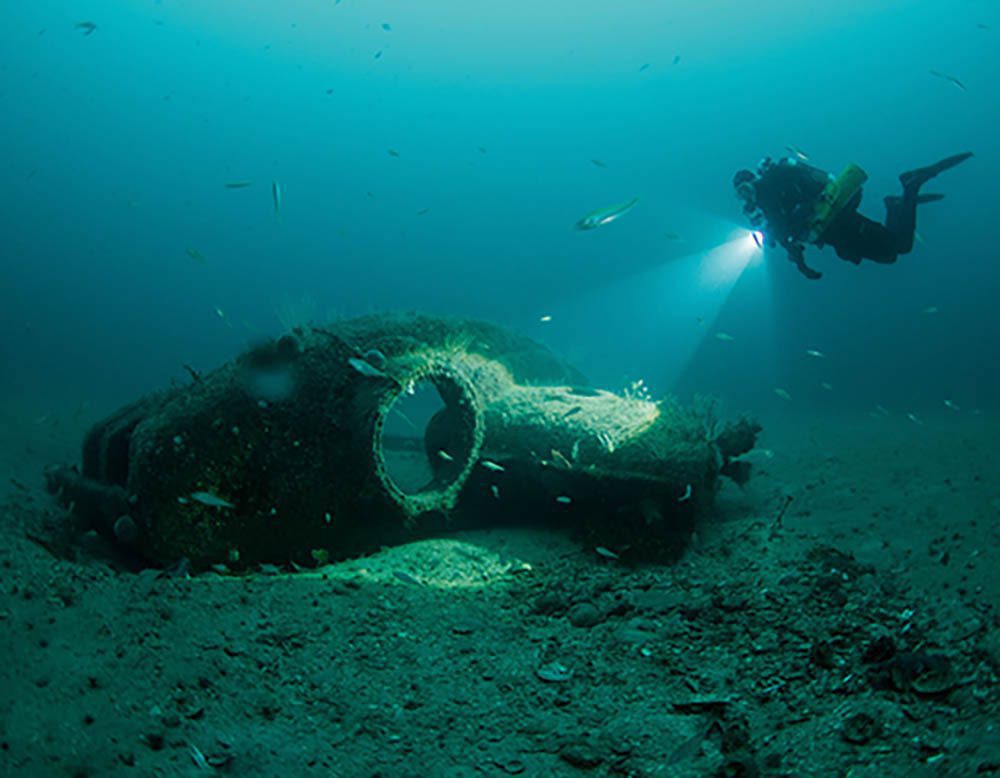

Scapa Flow 100
Scapa Flow ( / ˈskɑːpə, ˈskæpə /; from Old Norse Skalpaflói 'bay of the long isthmus') [1] is a body of water in the Orkney Islands, Scotland, sheltered by the islands of Mainland, Graemsay, Burray, [2] South Ronaldsay and Hoy. Its sheltered waters have played an important role in travel, trade and conflict throughout the centuries.

Diving the wreck of SMS Markgraf battleship, Scapa Flow YouTube
Scapa Flow Map Home Salvage Operations in Scapa Flow During the 1920s and 1930s the majority of the scuttled ships of the German High Seas Fleet were raised. It was one of the largest maritime salvage operations in history. Of the 52 ships that sank, only 7 remain beneath the waters of Scapa Flow.

Scapa Flow, the largest shipwreck graveyard in Europe
Scapa Flow Euphrau Elizabetha, 8 December 1710, stranded on Rysa Little Unknown, January 1728, wrecked on the west side of Holm of Houton Mary, brigantine, 5 February 1775, west of Holm Sound. William & Mary's Increase, 8 February 1799, wrecked between Stromness and Houton Captain Snow, 13 December 1854, stranded at Scapa Bay
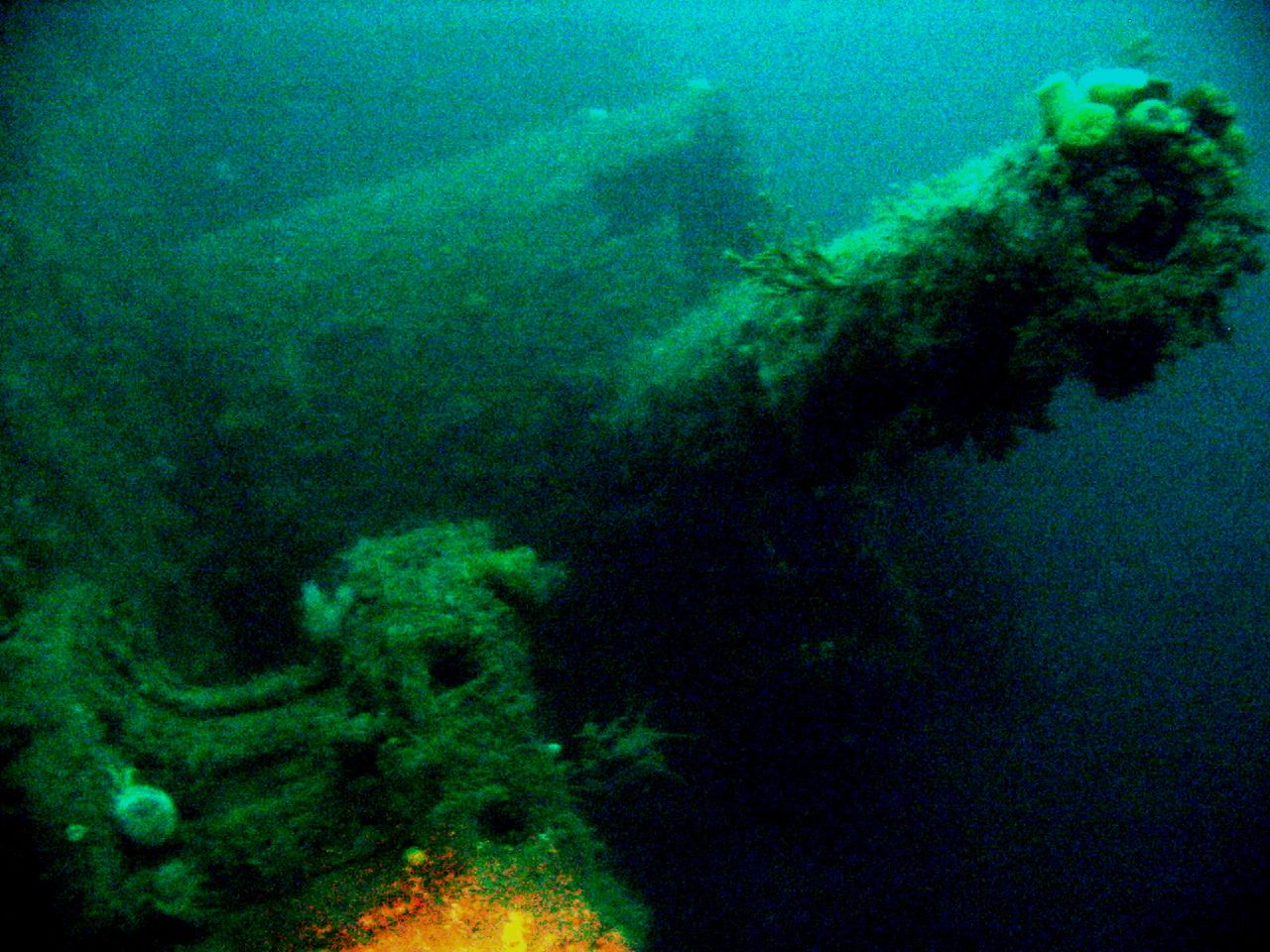
Scapa Flow wreck a photo on Flickriver
A major resource for salvage from 1919 to the 1970s, the wrecks now attract visitors from all over the world and contribute to the economy of Orkney. How we protect the wrecks. Since 2001, the remains of three battleships and four cruisers of the German High Seas Fleet scuttled in Scapa Flow in 1919 have been protected as scheduled monuments.

Go With The Flow Diving The Wrecks Of Scapa Flow
This crash was the longest emergency case in the Egyptian Air Force. Wing Commander Keraidy was the first Egyptian officer to be given the Golden Military Bravery Medal, first Category, without dying in a battle.. While the USS John F. Kennedy is operating ~100 miles NW of Scapa Flow, Scotland, as part of a 100 ship NATO naval exercise.
The GENES Blog Scapa Flow war wrecks mapped
At its deepest, Scapa Flow is 60m (197ft), although the deepest of the German wrecks lies in 47m (154ft). The site seems to have gained a reputation for being dark and murky. Visibility can be variable but is regularly in excess of 15m (50ft). The temperature can reach 19 Celsius (66F) at the surface in high summer, reducing with depth, so good.
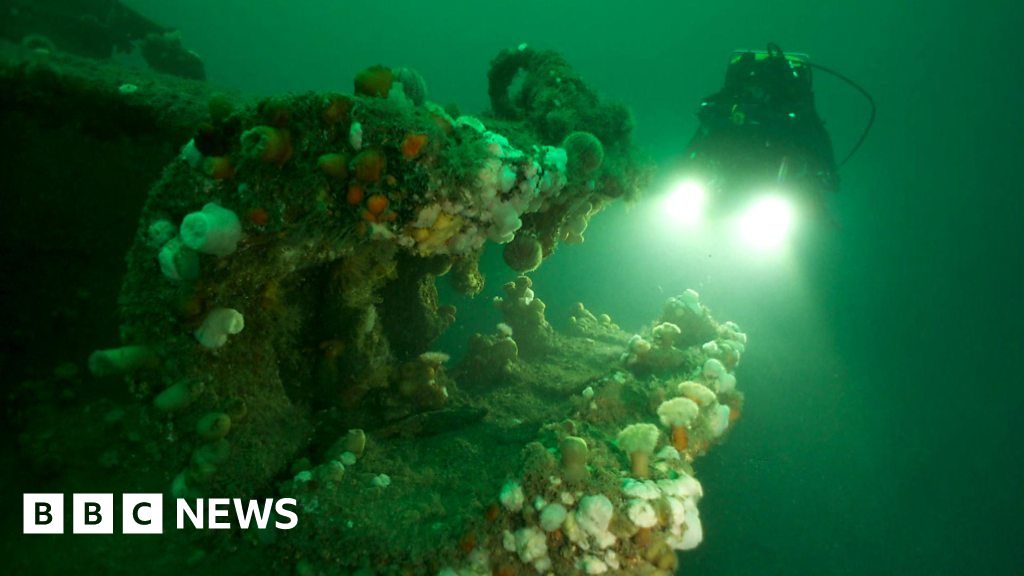

Divers map Scapa Flow wrecks ahead of centenary in 2019 BBC News
Instead the scuttling of the German High Seas Fleet in Scapa Flow was a deliberate act of sabotage ordered by a commander who refused to let his ships become the spoils of war. It was the.

Second diver in weeks dies at Scapa Flow while exploring Markgraf wreck Scotland The Times
Scuttling of the German fleet at Scapa Flow Coordinates: 58°54′N 3°11′W Shortly after the end of the First World War, the Imperial German Navy was scuttled by its sailors while held off the harbour of the British Royal Navy base at Scapa Flow, in the Orkney Islands of Scotland.

Scapa Flow wrecks how the scuttling of the German fleet after WWI crafted the Orkney diving
History of Scapa Flow: what happened, why it was important and where to see the remains - Countryfile.com Our guide looks at the history of Scapa Flow, including what happened and why it was a key moment in the First World War.

Iconic Scapa Flow wrecks sell but at a bargainbasement price 1 Magical places, Best
The German High Seas Fleet arrived in Scapa Flow on 23rd November 1918 when 74 German ships were interned there. On that day, almost the entire fleets of both Germany and the United Kingdom were anchored at Scapa Flow, it is known as perhaps one of the greatest naval phenomenon on the planet.

Eclectica Salvaging the German High Seas Fleet wrecks of Scapa Flow
HMS Royal Oak Royal Navy 833 killed: 14 October 1939: Scapa Flow: Capsized under 33 meters (108 ft) of water.: Royal Oak ' s bell is the centerpiece to a memorial to those who died aboard Royal Oak at St Magnus' Cathedral in Kirkwall.: Bretagne: French Navy: 977 killed: 3 July 1940: Mers-el-Kébir, Algeria: Scrapped: —. Kilkis: Royal Hellenic Navy: —. 23 April 1941: Salamis Naval Base.
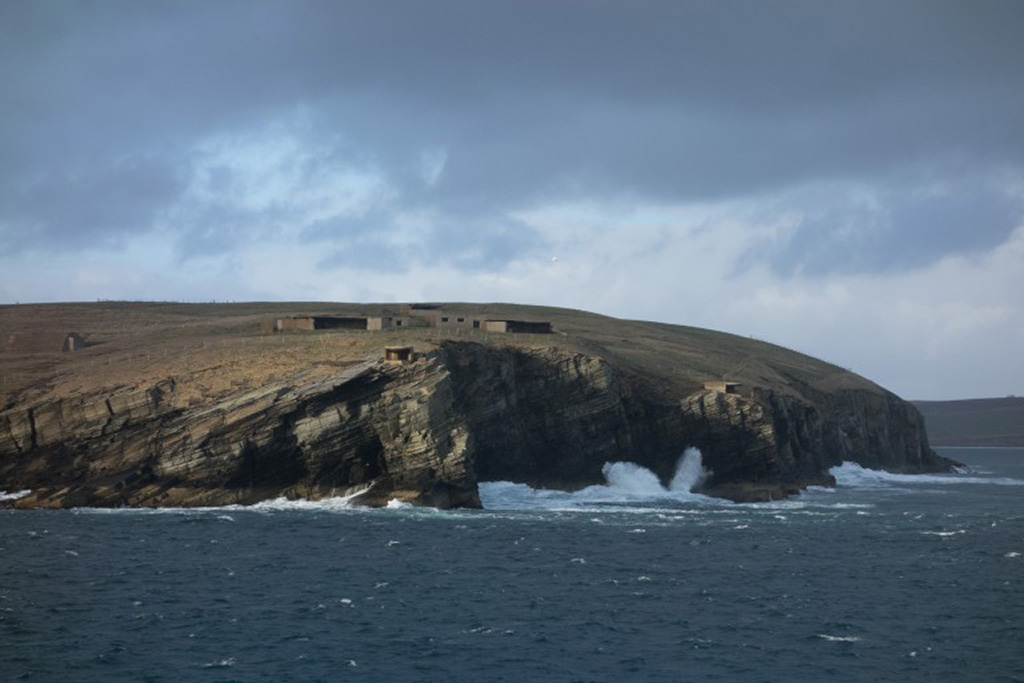

Coming up for air at Scapa Flow… Historic Environment Scotland
Scapa flow is well known to all divers around the world. This dive site has to be on your bucket list to dive. Scapa flow from the old Norse SKALPAFLOI is a.